Wall Dimensions In Building Construction: Essential Considerations
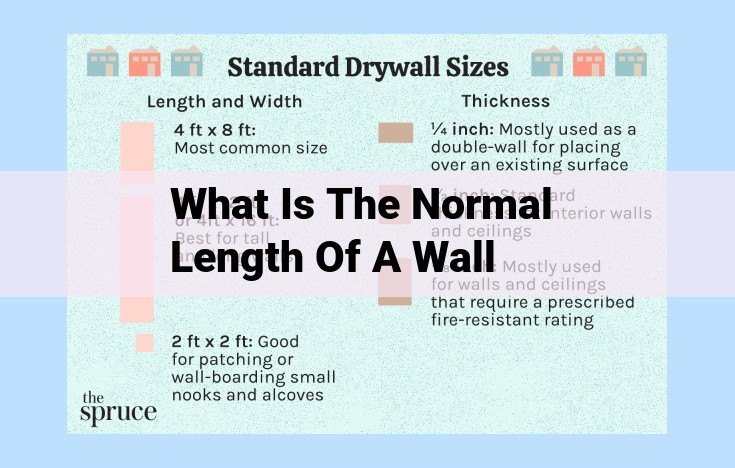
The normal length of a wall is not specified in the provided outline on building construction. This outline focuses primarily on structural elements, design aesthetics, environmental concerns, safety, and accessibility. It does not provide information on specific measurements or dimensions of building components.
Structural Elements: The Foundation of Building Construction
Building Codes and Regulations: The Blueprint for Safety and Design
In the realm of building construction, adherence to building codes and regulations is paramount. These regulations ensure the safety and stability of structures by outlining minimum standards for design, materials, and construction practices. By following these guidelines, builders can safeguard the well-being of occupants, protect property, and uphold public safety.
Wall Types: The Guardians of a Building’s Integrity
Walls serve as the primary support system for a building. Understanding the different types of walls is crucial for architects and engineers. Load-bearing walls carry the weight of the building, while curtain walls provide a non-structural enclosure. Shear walls resist lateral forces, such as earthquakes and wind loads, ensuring the building’s stability. Choosing the appropriate wall type is essential for the structural integrity of any construction project.
Material Considerations: The Building Blocks of Strength and Durability
The selection of building materials has a profound impact on a structure’s performance. Concrete’s strength and fire resistance make it ideal for foundations and structural elements. Steel’s high strength-to-weight ratio allows for lightweight and durable structures, while wood’s versatility and cost-effectiveness make it a popular choice for framing and roofing. Masonry’s thermal insulation and soundproofing properties enhance the comfort and energy efficiency of buildings.
Structural Engineering: The Masterminds of Structural Stability
Structural engineers play a critical role in ensuring the stability of buildings. They analyze loads, forces, and materials to design structures that can withstand various environmental and эксплуатационных conditions. Their expertise ensures that buildings can safely support their intended use and resist potential hazards, such as earthquakes and storms.
Design and Aesthetics: The Art of Building
When it comes to building construction, the process of design goes beyond mere functionality. It’s where artistry and science intertwine to create structures that not only serve their purpose but also captivate the senses.
Architectural Design: A Symphony of Form and Function
Architectural design is a complex undertaking that considers a myriad of factors, from the practical to the aesthetic. Architects must strike a delicate balance between:
- Functionality: Designing spaces that meet the specific needs of the occupants.
- Aesthetics: Creating visually appealing structures that enhance the surrounding environment.
- Environmental consciousness: Incorporating sustainable design principles to minimize the building’s environmental impact.
The Process of Architectural Design
The architectural design process typically follows a series of steps:
- Concept development: The architect works closely with the client to understand their vision and requirements.
- Schematic design: Preliminary sketches and plans outline the basic form and layout of the building.
- Design development: The design is further refined, with detailed drawings and specifications.
- Construction drawings: The final set of plans provides precise instructions for the construction team.
Throughout the process, the architect considers factors such as:
- Site analysis: The location, orientation, and surrounding environment.
- Building materials: The choice of materials will impact both the aesthetic and functional aspects of the building.
- Construction techniques: The methods used to construct the building will influence its durability and cost-effectiveness.
By skillfully weaving together these elements, architects create structures that not only fulfill their intended purpose but also inspire wonder and enhance the human experience.
Environmental Concerns in Building Construction: Embracing Sustainability
In today’s era of environmental consciousness, building construction plays a vital role in safeguarding our planet. Architects and engineers are increasingly embracing sustainable practices to reduce the environmental impact of buildings. One critical aspect of this is insulation and energy efficiency.
Insulation: A Key to Energy Savings
Insulation is crucial for minimizing heat loss and gain, thereby reducing energy consumption. Insulation materials such as fiberglass, cellulose, and spray foam create a barrier between the interior and exterior of a building, preventing heat from escaping in winter and entering in summer.
Materials and Techniques for Insulation
Choosing the right insulation material and installation technique is essential. Fiberglass is a popular and cost-effective option, while cellulose is environmentally friendly and made from recycled paper. Spray foam provides excellent air sealing but can be more expensive.
Proper installation is equally important. Gaps and air leaks compromise insulation’s effectiveness, so ensuring a tight seal is crucial. This can be achieved through techniques such as taping seams and applying caulk around windows and doors.
By investing in quality insulation, building owners can significantly reduce their energy bills and contribute to environmental conservation. Well-insulated buildings are more comfortable, healthier, and more sustainable.
Safety and Accessibility: Vital Considerations in Building Construction
In the realm of building construction, ensuring the safety and accessibility of occupants is paramount. These aspects go beyond mere compliance with codes and regulations; they represent a fundamental commitment to protecting lives and empowering individuals.
Fire Safety: A Shield Against Catastrophic Events
Fire safety measures are not simply afterthoughts; they are indispensable safeguards that can prevent tragedies. Building codes mandate the use of fire-rated materials to minimize the spread of flames, while fire sprinklers act as automatic guardians, suppressing fires before they escalate. Escape routes provide clear paths to safety, ensuring quick evacuation in emergencies.
Accessibility Standards: Inclusion for All
Accessibility is not a privilege; it is a fundamental right. Building construction must prioritize inclusivity by incorporating features that enable people with disabilities to navigate and use buildings comfortably. Ramps provide seamless access for wheelchairs, elevators transport individuals to different floors effortlessly, and accessible features such as wide doorways and grab bars enhance mobility and independence.
By adhering to fire safety and accessibility standards, buildings become not just structures but sanctuaries that safeguard and empower all who enter. These measures are not merely legal obligations but moral imperatives, ensuring that every individual has the opportunity to live, work, and enjoy public spaces with dignity and ease.