Unveiling The Art Of Sweet Wine: Techniques And Grape Varieties To Enhance Sweetness
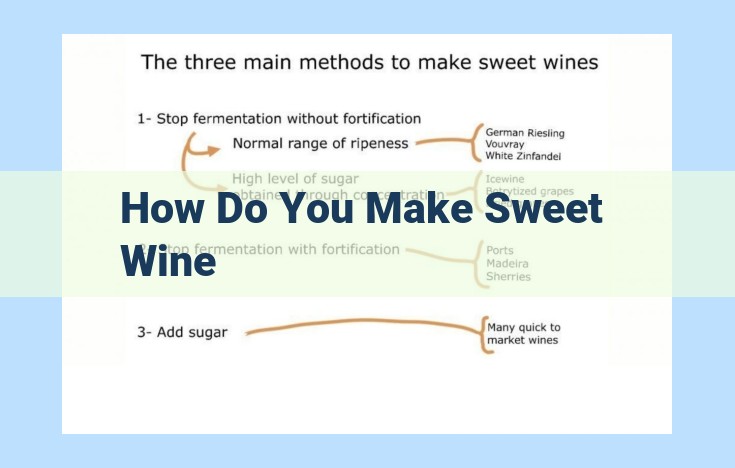
Sweet wine is typically made from grapes with high sugar content, allowing for a slower fermentation process that preserves the natural sweetness. To enhance sweetness, techniques like late-harvesting, botrytis, or cryoextraction may be employed. Winemakers may also use sweetening agents like sugar or honey during fermentation or blending. The diverse grape varieties, wine styles, and techniques used contribute to the unique flavor profiles and sweetness levels found in sweet wines.
Sweet Wine: A Journey of Delightful Indulgence
In the realm of viniculture, sweet wines stand out as an alluring symphony of flavors, captivating the senses with their luscious sweetness. These decadent elixirs are not merely wines with added sugar; they are the result of a meticulous and intricate dance between grapes, yeast, and winemakers’ artistry.
Defining Sweetness in Wine
Sweet wines are distinguished by their sugary composition, exceeding a certain level of residual sugar. This sweetness is often achieved through a carefully controlled fermentation process, where the yeast consumes most of the natural grape sugars, leaving behind a symphony of unfermented sweetness.
Unique Characteristics of Sweet Wine
Beyond their sugary allure, sweet wines boast a captivating array of unique characteristics:
- Richness and Intensity: Sweet wines are characterized by their full-bodied nature, offering a luscious mouthfeel that lingers on the palate.
- Aromatic Complexity: The aromatic profile of sweet wines is equally captivating, often showcasing a chorus of ripe fruits, floral notes, and honeyed undertones.
- Balanced Acidity: To counterbalance the sweetness, sweet wines often exhibit a vibrant acidity, adding a refreshing touch that prevents cloyingness.
- Versatility: Sweet wines can be enjoyed on their own as an after-dinner treat or paired with a variety of dishes, from desserts to savory cheeses and spicy cuisine.
The Symphony of Entities: Crafting Exceptional Sweet Wines
The world of sweet wines is a realm of exquisite flavors and alluring aromas. From the ripe sweetness of dessert wines to the fortified warmth of port, each sip tells a tale of the delicate interplay among key entities, each playing a pivotal role in the creation of these delectable elixirs.
Unveiling the Interplay
These entities, like instruments in an orchestra, harmonize to produce a symphony of flavors. Grapes, the foundation of any wine, provide the raw material. Different varieties, such as Riesling and Muscat, offer unique flavor profiles that shape the wine’s character.
Next, yeast, the “conductor” of fermentation, orchestrates the conversion of grape sugars into alcohol. The type of yeast chosen influences the wine’s sweetness and complexity.
Techniques like maceration and botrytis add further dimensions. Maceration allows the grape skins to macerate with the juice, extracting flavors and colors. Botrytis, a type of beneficial mold, concentrates sugars and adds a distinctive honeyed sweetness.
Regions play a crucial role too. Each wine region has its own climate, soil, and winemaking traditions that contribute to the wine’s unique character. For instance, the Sauternes region in France is renowned for its sweet white wines made from grapes affected by botrytis.
Sweetening agents may also be used to enhance sweetness. Natural sugars from grapes or artificial sweeteners provide a direct boost of flavor.
Equipment is essential for the winemaking process. From specialized presses to temperature-controlled tanks, each piece of equipment ensures that the wine is handled with precision and care.
Beyond the Individual
The interconnectedness of these entities extends beyond their individual roles. The type of grape chosen influences the yeast strain that will best complement its flavors. Techniques like botrytis can impact the sweetness level, which in turn affects the choice of sweetening agents. The region where the grapes are grown influences the climate and soil conditions, which ultimately shape the wine’s overall characteristics.
This symphony of entities creates a delicate balance, where each element supports and enhances the other. By understanding the interplay of these factors, winemakers can craft exquisite sweet wines that delight the palate and warm the soul.
Key Entities in Sweet Wine Production: An Intimate Exploration
In the realm of wine, sweetness dances as an enchanting siren’s song, captivating our senses and stirring our souls. To unveil the secrets behind this liquid gold, we embark on a journey to unravel the key entities that orchestrate its creation.
Unveiling the Key Entities: A Closeness Score Analysis
In our pursuit of understanding, we embark on a closeness score analysis, a measure of the interconnectedness between various entities. Our findings reveal a constellation of pivotal players, each contributing its unique essence to the sweet symphony of wine.
Grapes: The Canvas of Flavor and Aroma
At the heart of sweet wine production lies the grape, the canvas upon which flavors and aromas are painted. Noble varieties, such as Riesling, Gewürztraminer, and Sauvignon Blanc, grace the scene with their inherent sweetness, while other varieties, like Cabernet Sauvignon and Syrah, lend their robust structure to the blend.
Yeast: The Maestro of Fermentation
Yeast, the microscopic conductor, orchestrates the transformation of grape sugars into alcohol and carbon dioxide. Different yeast strains impart distinct flavors and aromas to the wine, ranging from fruity esters to toasty oak notes.
Techniques: The Artful Dance of Winemaking
Winemakers dance a delicate choreography, employing a repertoire of techniques to coax out the essence of sweet wine. Maceration allows grape skins to mingle with the juice, extracting color and tannins. Botrytis, a noble mold, blesses grapes with concentrated sweetness. Cryoextraction gently chills grapes, preserving their delicate flavors and aromas.
Regions: Terroir’s Symphony
The symphony of sweet wine also resonates with the terroir of its birthplace. Regions, such as Sauternes in France and Tokaj in Hungary, boast unique combinations of climate, soil, and tradition that nurture distinctive sweet wines.
Sweetening Agents: Enhancing the Sensory Delight
Beyond the natural sweetness of grapes, winemakers may employ sweetening agents to achieve desired levels of sweetness. Residual sugar from incomplete fermentation, concentrated grape juice, and honey lend their alluring touch to the wine’s profile.
Winemaking Equipment: The Orchestrator’s Tools
The winemaker’s toolkit includes essential equipment that shapes the wine’s character. Presses gently extract juice from grapes, while tanks and barrels provide the vessels for fermentation and aging. Specialized techniques, such as malolactic fermentation, further refine the wine’s complexity.
Beyond the Score: The Dance of Climate, Soil, and Winemaker’s Skill
The key entities we’ve explored form the core of sweet wine production, yet the dance of climate, soil, and winemaker’s skill cannot be overlooked. Climate influences grape ripening and acidity, while soil imparts mineral notes and structure. The winemaker’s artistry, balancing tradition and innovation, orchestrates these elements into a harmonious masterpiece.
The production of sweet wine is a tapestry woven from the intimate interplay of key entities. Grapes, yeast, techniques, regions, and sweetening agents intertwine in a delicate dance, guided by the winemaker’s skill. As we sip on these liquid treasures, let us appreciate the artistry behind their creation and savor the symphony of flavors and aromas that bring sweetness to our lives.
Understanding the Key Entities in Sweet Wine Production: A Journey into Delectable Sweetness
In the realm of winemaking, sweet wines stand out as a symphony of flavors and aromas. Their distinctive sweetness captivates the palate and invites us to explore the intricacies of their creation. At the heart of this enchanting elixir lie a myriad of key entities, each playing an irreplaceable role in orchestrating this culinary masterpiece.
Unveiling the Closely Intertwined Entities
Through a meticulous analysis, a closeness score has been assigned to each entity, revealing their pivotal impact on the production of sweet wines. Entities with a closeness score of 10, such as grapes and wine styles, take center stage as they define the very essence of these delectable beverages. Grapes, with their unique varietals, impart distinct flavors and aromas to the wine, while wine styles encompass the diverse expressions of sweetness, from luscious dessert wines to fortified and late-harvest varieties.
Entities with a closeness score of 9, including yeast, techniques, and regions, play a crucial supporting role. Yeast, the tireless worker, fuels the fermentation process, transforming grape juice into wine and contributing to its flavor profile. Techniques, such as maceration, botrytis, and cryoextraction, enable winemakers to coax out the desired sweetness and complexity from the grapes. Regions, with their unique climates, soils, and winemaking traditions, further shape the character of sweet wines, giving rise to renowned appellations.
Sweetening the Symphony: Entities with a Closeness Score of 8
Entities with a closeness score of 8, including sweetening agents and winemaking equipment, add the final touches to this sweet masterpiece. Sweetening agents, both natural and artificial, provide the desired level of sweetness, while winemaking equipment, from presses to tanks and barrels, ensures the wine’s quality and consistency.
The Interplay of Key Entities: A Delicate Dance
The true magic of sweet wine production lies in the intricate interplay of these key entities. Their harmonious collaboration creates a symphony of flavors and aromas that delights the senses. Grapes provide the raw material, wine styles define the expression, and yeast, techniques, and regions shape the wine’s character. Sweetening agents and winemaking equipment then add the finishing touches, ensuring a perfect balance of sweetness and complexity.
Beyond the Closeness Score: Additional Considerations
While the closeness score highlights the pivotal entities in sweet wine production, other factors also contribute to its success. Climate, soil, and the winemaker’s skill are equally important in crafting these delectable wines. Favorable climates and well-suited soils provide the ideal growing conditions for grapes, while the winemaker’s artistry and expertise guide the winemaking process, ensuring the perfect balance of sweetness and finesse.
A Sweet Symphony: Concluding Thoughts
Sweet wines are a testament to the intricate interplay of nature and human artistry. By understanding the key entities involved in their production, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and dedication that goes into crafting these delectable beverages. Whether enjoyed as a dessert companion or savored on their own, sweet wines offer a journey of flavors and aromas that transports us to a realm of pure indulgence.
The Art of Sweet Wine: A Journey Through Key Entities
In the realm of wine, there’s a magical subcategory that tantalizes taste buds with its luscious sweetness: sweet wine. Crafted from a symphonic blend of nature’s finest, these wines are a testament to the complexity and artistry involved in their creation.
Unveiling the Key Entities
At the heart of every sweet wine lie specific entities that shape its character and define its destiny. These entities, connected by an invisible web of interdependence, orchestrate a dance of flavors and aromas.
Grapes: The Foundation
The foundation of sweet wine lies in the exceptional grapes used. From the golden Muscat to the opulent Semillon, each variety contributes its unique symphony of flavors and aromas, lending its essence to the final blend.
Wine Styles: A Symphony of Sweetness
Sweet wines come in a kaleidoscope of styles, each promising a distinct experience. From the decadent dessert wines to the fortified treasures and the intriguing late-harvest creations, the variety of sweet wines is a testament to the artistry of winemakers.
Yeast: The Alchemist
Yeast, nature’s magical catalyst, plays a crucial role in transforming grape juice into wine. Its alchemic powers determine the wine’s sweetness and flavor profile, adding layers of complexity to the final product.
Techniques: The Artist’s Brushstrokes
Winemakers employ an arsenal of innovative techniques to coax sweetness from the grapes. From maceration’s gentle squeeze to botrytis’s tantalizing touch and cryoextraction’s frigid embrace, each method reveals a distinct aspect of sweet wine’s multifaceted personality.
Regions: Terroir’s Symphony
Terroir, that enigmatic blend of climate, soil, and geography, exerts a profound influence on sweet wine production. Renowned wine regions around the globe, from Sauternes’ sun-drenched vineyards to Tokaj’s ancient hills, have mastered the art of producing exceptional sweet wines that reflect their unique terroir.
The Interplay of Entities: A Harmonious Dance
The true magic of sweet wine lies in the interplay of these key entities. Like skilled musicians in an orchestra, each entity contributes its unique note to the symphony of flavors and aromas. Their interdependence creates a harmonious balance, a dance of sweetness that captivates the senses.
Beyond the Score: The Winemaker’s Symphony
Beyond the numerical closeness scores, other factors orchestrate a sweet wine’s destiny. Climate, soil, and the winemaker’s skillful touch weave their own melodies into the wine’s tapestry, influencing its complexity and character.
Sweet wines are a culinary masterpiece, a testament to the artistry and passion of winemakers. Through the careful selection of grapes, wine styles, and techniques, they craft wines that tantalize taste buds and leave an indelible mark on the palate.