Ultimate Guide To Keep Squirrels Away: Humane And Effective Methods
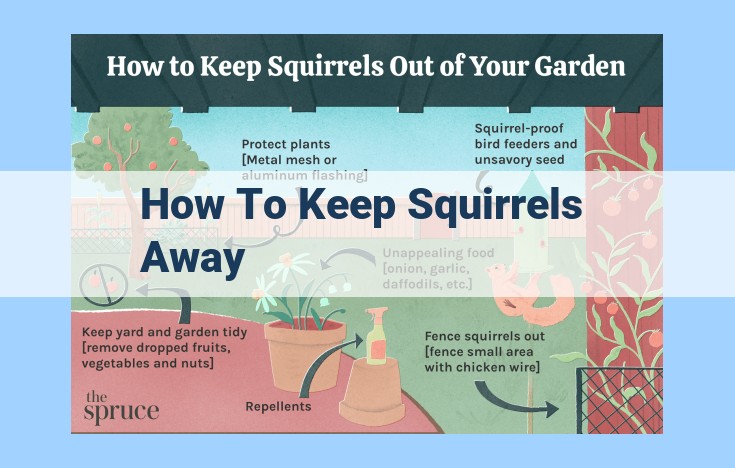
Keep squirrels away by using physical barriers (fences, screens), protective barriers (mesh covers for feeders), and noise deterrents (motion-activated devices, ultrasonic deterrents). Chemical repellents can also be effective, but choose humane options. Remove food sources, seal entry points, and consider predator decoys to deter squirrels. If needed, consider traps or professional pest control services. Remember safety and legal implications, and prioritize humane and effective methods.
- State the purpose of the blog post: to provide comprehensive information on controlling squirrels.
Controlling Squirrels: A Comprehensive Guide
Are you tired of the rampaging squirrels in your backyard, gnawing on your bird feeders and wreaking havoc on your garden? If so, you’re not alone. Squirrels can be a nuisance to property owners, but controlling them doesn’t have to be a challenge. This comprehensive guide will provide you with all the information you need to effectively manage your squirrel population.
Squirrel Biology and Behavior
Understanding squirrel biology and behavior is crucial for effective control. Squirrels are agile climbers and can quickly access your property through trees and fences. They are also opportunistic feeders, consuming various foods, including nuts, seeds, and fruits. By understanding their habits, you can anticipate their movements and develop targeted control measures.
Physical Deterrents
Physical deterrents are a non-lethal way to keep squirrels away from your property. Fences and screens can prevent them from accessing gardens and bird feeders. Tree wraps can protect trees from gnawing damage. By creating physical barriers, you can make your property less appealing to squirrels.
Noise and Chemical Deterrents
Noise and chemical deterrents can frighten or repel squirrels. Motion-activated devices emit loud noises when triggered, while ultrasonic deterrents emit high-pitched sounds that humans can’t hear but squirrels find irritating. Chemical repellents contain scents that squirrels find unpleasant, making them avoid treated areas.
Habitat Modification and Management
Modifying the habitat around your property can discourage squirrels from taking up residence. Remove or relocate squirrel nests, seal entry points into buildings, and minimize food sources. By making your property less hospitable, you can reduce squirrel activity. Predator decoys, such as fake owls or snakes, can also deter squirrels.
Repellents and Removal
Squirrel repellents come in various forms, including granular, liquid, and spray. They can be applied to plants, bird feeders, and other areas where squirrels are known to frequent. Traps can be used to capture squirrels if other methods are ineffective. However, it’s essential to ensure that traps are placed and used humanely, and that all relevant local laws are followed.
Safety and Legal Considerations
When dealing with squirrels, always prioritize safety. Wear protective clothing to avoid bites or scratches. Be aware of any local regulations regarding squirrel removal or harm to ensure compliance. Consulting with a professional wildlife management agency or pest control company can provide valuable guidance and support.
Controlling squirrels can be a challenge, but with a comprehensive approach, you can effectively manage their population. By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, you can protect your property, garden, and bird feeders from these crafty creatures. Remember to prioritize humane and effective methods to ensure the well-being of both squirrels and your surroundings.
Squirrel Biology and Behavior: Understanding the Habits and Risks
Squirrels, with their bushy tails and inquisitive nature, are a common sight in many neighborhoods. While they can be charming to observe, their presence can also present challenges for homeowners. To effectively control these furry visitors, it’s essential to gain a comprehensive understanding of their biology and behavior.
Squirrels belong to the Rodentia order, which also includes rats and mice. They are highly adaptable and can thrive in diverse habitats, from forests to urban areas. There are several squirrel species, including tree squirrels, flying squirrels, and ground squirrels, each with its unique characteristics and habitat preferences.
One of the key aspects of squirrel behavior is their food-caching habits. Squirrels collect and store nuts, seeds, and other food items for later consumption. These stashes, often hidden in tree hollows or underground, help them survive during periods of food scarcity.
Understanding squirrel diet is crucial for effective control measures. Squirrels are omnivorous, consuming a wide range of plant and animal matter. Plant-based foods, such as nuts, fruits, and seeds, form the majority of their diet. However, they will also opportunistic predators of small insects, birds’ eggs, and even baby birds.
Potential Risks Associated with Squirrels
While squirrels can be entertaining to watch, their activities can pose risks to property and human health:
- Structural Damage: Squirrels can chew on wires, damage insulation, and create entry points for other pests.
- Electrical Hazards: Squirrel chewing on electrical wires can lead to short circuits or fires.
- Disease Transmission: Squirrels can carry diseases such as rabies, tularemia, and salmonellosis, which can be transmitted to humans through bites or contact with contaminated surfaces.
- Parasite Infestations: Squirrels can harbor parasites such as fleas and ticks, which can infest homes and pose health risks to pets and humans.
By understanding squirrel biology and behavior, homeowners can develop informed strategies for managing these creatures and minimizing the potential risks associated with their presence.
Physical Deterrents: Keeping Squirrels at Bay
In the battle against persistent squirrels, physical deterrents stand as a formidable defense against their acrobatic antics.
Fences: A Boundary They Can’t Cross
Like seasoned border guards, fences present an unyielding barrier, keeping squirrels from infiltrating your property. Chain-link fences, with their tightly woven links, prove particularly effective, while sturdy wooden fences, with their solid planks, offer an equally daunting challenge. Measuring at least 6 feet tall, these fences make it practically impossible for squirrels to scale or jump over.
Screens: Invisible Shields for Your Plants
For delicate plants and shrubs, mesh screens provide a protective cloak, shielding them from curious squirrels. Made from lightweight fiberglass or metal, these screens can be draped over plants during the day and removed at night, allowing for ample sunlight.
Tree Wraps: Protecting Trunks from Climbs
Squirrels, known for their tree-climbing prowess, can wreak havoc on bark. Tree wraps come to the rescue by creating a physical barrier around the trunk, preventing squirrels from getting a foothold. These wraps, typically made from durable plastic or metal, should extend at least 3 feet high and be securely fastened to prevent determined squirrels from peeling them off.
Protective Barriers: Shielding Food Sources
To protect bird feeders and fruit trees, consider erecting mesh covers. Resembling miniature cages, these covers prevent squirrels from reaching the food inside while allowing birds and other wildlife to enjoy their treats unhindered.
Noise and Chemical Deterrents: Keeping Squirrels at Bay
When squirrels become a nuisance in your garden or home, it’s time to consider deterrents. Noise and chemical deterrents offer effective solutions to keep these furry critters away without causing them harm.
Noise Deterrents: Making a Ruckus that Squirrels Hate
Motion-activated devices, ultrasonic deterrents, and loud noises can create an uncomfortable environment for squirrels. Motion-activated devices emit a spray of water or a startling noise when they detect movement. These devices are particularly effective in areas where squirrels frequently visit, such as bird feeders or gardens.
Ultrasonic deterrents emit high-pitched sounds that are inaudible to humans but irritating to squirrels. These devices can be placed in areas where squirrels congregate, such as attics or crawl spaces. However, their effectiveness can vary depending on the squirrel’s species and individual tolerance.
Loud noises, such as banging pots and pans or playing loud music, can temporarily scare squirrels away. However, this method is not advisable for prolonged use as it can become disruptive to both you and your neighbors.
Chemical Repellents: Scent-Based Deterrents
Chemical repellents use strong scents to deter squirrels from approaching certain areas. These repellents come in various forms, including granular, liquid, and spray. Granular repellents can be sprinkled around gardens or bird feeders, while liquid and spray repellents can be applied to surfaces or objects that squirrels find attractive.
The active ingredients in chemical repellents vary, but they typically contain capSICUm (cayenne pepper), peppermint oil, or ammonia. These scents are unpleasant to squirrels and can create a barrier that they are hesitant to cross.
When using chemical repellents, it’s important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Reapply the repellent as needed, especially after rainfall or heavy watering. Also, keep pets and children away from treated areas to avoid accidental ingestion.
Habitat Modifications and Management: A Comprehensive Approach to Squirrel Control
Understanding the habits of squirrels is crucial for effective control measures. A key component is habitat modification, which involves modifying the environment to reduce their attractions and discourage their presence.
One approach involves removing or relocating squirrel nests. Identify and destroy active nests during the winter months when squirrels are less active. Additionally, seal entry points around your home by covering holes and gaps where squirrels might sneak in.
Another effective strategy is minimizing food sources. Squirrels are opportunistic feeders, so removing potential food sources, such as bird feeders, fruit trees, and compost piles, will reduce their incentive to visit your property.
Predator Decoys and Wildlife Management Support
Complementing habitat modifications, consider using predator decoys. Fake owls or snakes can create an illusion of danger, deterring squirrels from approaching.
If DIY methods prove insufficient, don’t hesitate to contact wildlife management agencies. These organizations can provide guidance, support, and even assist with squirrel removal in certain cases.
Professional Squirrel Removal: When to Call in the Experts
When all else fails, professional pest control companies offer specialized services for squirrel removal. Their expertise and safe practices ensure effective and humane control measures.
Repellents and Removal: Taking Control of Squirrels
Squirrel Repellents: A Chemical Barrier
When physical deterrents fail, chemical repellents offer an effective line of defense against invading squirrels. These products come in various forms, including granular, liquid, and spray. Each type has its advantages and effectiveness against specific squirrel species.
Traps: A Humane Approach to Removal
In situations where repellents prove insufficient, traps provide a humane solution for squirrel removal. Live traps, such as cage-style or box traps, allow for safe capture without causing harm. Proper placement of traps is crucial, and they should be baited with foods that squirrels find alluring. Once captured, squirrels should be released far from populated areas to prevent them from returning.
Additional Safety Considerations
When dealing with traps, it’s essential to exercise caution. Always wear gloves and avoid direct contact with squirrels to minimize the risk of bites or diseases. Additionally, it’s important to familiarize yourself with local laws and regulations regarding squirrel removal and harm to ensure compliance.
Safety and Legal Considerations
When attempting to control squirrels, it’s crucial to prioritize safety and adhere to legal regulations. These considerations ensure the well-being of both humans and animals while minimizing potential risks and legal consequences.
Safety Considerations
- Bites and Scratches: Squirrels, though small, can deliver painful bites. Always wear gloves when handling squirrels or their nests to avoid injury.
- Diseases: Squirrels can carry diseases such as rabies, tularemia, and salmonella. If bitten or scratched, seek medical attention promptly.
- Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to squirrel urine or feces. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
Legal Implications
- Protected Species: In certain areas, squirrels may be protected by local or state laws. It’s illegal to harm or remove squirrels in these locations.
- Trapping Regulations: Trapping laws vary widely. Ensure you have proper permits and comply with all regulations regarding trap placement, timing, and release protocols.
- Humane Removal: Methods for controlling squirrels should be humane and minimize animal suffering. Avoid poison or inhumane traps that cause unnecessary pain or death.
It’s essential to check with your local wildlife agency or pest control professional for specific regulations and guidance in your area. By adhering to safety precautions and legal guidelines, you can effectively manage squirrel populations while protecting both human and animal well-being.